What are 12 different job roles & responsibilities in Data Science?
Are you a person who is planning to switch into the field of Analytics but is confused about what roles you want to pursue your career in? Well, you are at the right place. This article is targeted at a newbie audience who is planning to make a move into this field. We have collated the different roles in Data science and analytics, the skill sets required for the role, and the nature of the respective role’s work. In the earlier article, we have explained the life cycle of data science and recommend reading it.
Before attempting some hard-and-fast role definitions of these data science careers, let us start by sketching out the different task sets you typically find on a data science team. The idea here is to scope the high-level competence areas that need to be covered on a data science team, regardless of who carries out which task.
The three main data science careers are:
- Mathematics/Statistics
- Computer Science
- Business domain knowledge.
Competence areas are needed on a data science team.
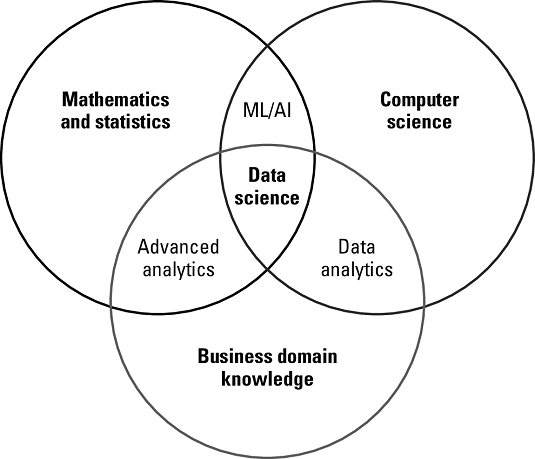
The image above shows the easy part because there’s general agreement on which competencies are required for a successful and efficient data science career though you still need to define the roles and areas of responsibility for each team member. The definitions of the data science career that you find here aim to give you a general understanding of the most important roles you will need on your data science team. Remember that variants may apply depending on your specific setup and strategic focus.
Some companies require you to know all the skills of all these positions, but as your team grows at your company, you may find that certain people will focus on their strengths to ultimately solve the most problems with Data Science and therefore become specialized in one of the roles below.
- Business Analyst
- Database Administrator
- Big Data Engineer/Data Architect
- Data Analyst
- ML Engineer
- Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Statistician
- Data Scientist
- Computer Vision(CV) Engineer
- Natural Langauge Processing(NLP) Engineer
- MLOps Engineer
Business Analyst

The role of business analysts is slightly different from other data science jobs. While they do have a good understanding of how data-oriented technologies work and how to handle large volumes of data, they also separate the high-value data from the low-value data. In other words, they identify how Big Data can be linked to actionable business insights for business growth.
Although many of their job tasks are similar to that of data analysts, business analysts are experts in the domain they work in. They try to narrow the gap between business and IT. Business analysts provide solutions that are often technology-based to enhance business processes, such as distribution or productivity.
Organizations need these “information conduits” for a plethora of things such as gap analysis, requirements gathering, knowledge transfer to developers, defining scope using optimal solutions, test preparation, and software documentation.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Business analysts identify business needs, crystallizing the data for easy understanding, manipulation, and analysis via clear and precise requirements documentation, process models, and wireframes. They identify key gaps, challenges, and potential impacts of a solution or strategy.
- In a day, a business analyst could be doing anything from defining a business case or eliciting information from top management to validating solutions or conducting quality testing. Business analysts need to be effective communicators and active listeners, resilient and incisive, to translate tech-speak or statistical analysis into business intelligence.
- They use predictive, prescriptive, and descriptive analyses to transform complex data into easily understood actionable insights for the users. A change manager, a process analyst, and a data analyst could be doing business analysis tasks in everyday work.
Skills Required:
- Apart from a degree in business administration in the field of your choice, healthcare or finance, aspiring business analysts need to have knowledge of data visualization tools such as Tableau and requisite IT know-how, including database management and programming.
- You could also major in computer science with additional statistics, organizational behavior, and quality management courses. Or you could get professional certifications such as the Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP®) or PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PBA). Many universities offer degrees in business intelligence, business analytics, and analytics. Check out the courses in the U.S/India.
How to Become a Business Analyst?
Business analysts act as a link between the data engineers and the management executives. So, they should understand business finances and business intelligence, and also the IT technologies like data modeling, data visualization tools, etc
Database Administrator
The job profile of a database administrator is pretty self-explanatory- they are responsible for the proper functioning of all the databases of an enterprise and grant or revoke its services to the company employees depending on their requirements. They are also responsible for database backups and recoveries
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Build database systems of high availability and quality depending on each end user’s specialized role
- Design and implement database in accordance to end users’ information needs and views
- Define users and enable data distribution to the right user in the appropriate format and in a timely manner
- Use high-speed transaction recovery techniques and backup data
- Minimize database downtime and manage parameters to provide fast query responses
- Provide proactive and reactive data management support and training to users
- Determine, enforce and document database policies, procedures, and standards
- Perform tests and evaluations regularly to ensure data security, privacy, and integrity
- Monitor database performance, implement changes, and apply new patches and versions when required
Skills Required:
- Hands-on experience with database standards and end-user applications
- Excellent knowledge of data backup, recovery, security, integrity, and SQL
- Familiarity with database design, documentation, and coding
- Previous experience with DBA case tools (frontend/backend) and third-party tools
- Familiarity with programming languages API
- Problem-solving skills and ability to think algorithmically
How to Become a Database Administrator?
Some of a database administrator’s essential skills and talents include database backup and recovery, data security, data modeling, design, etc. If you are good at disaster management, it is certainly a bonus.
Big Data Engineer

Knowledge of different programming and scripting languages is a non-negotiable skill. Usually, people with 1 to 3 years of experience handling databases and software development are preferred for an entry-level position.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Big data engineers develop, maintain, test, and evaluate big data solutions within organizations.
- They are also involved in the design of big data solutions because of their experience with Hadoop [-] based technologies such as MapReduce, Hive, MongoDB, or Cassandra.
- Big data engineers configure, use, and program big data solutions to support big data analysts and meet business requirements via customization and optimization of features.
- Using various open-source tools, they “architect highly scalable distributed systems.” They must integrate data processing infrastructure and data management.
- It is a highly cross-functional role. With more years of experience, the responsibilities in development and operations; policies, standards, and procedures; communication; business continuity and disaster recovery; coaching and mentoring; and research and evaluation increase.
Skills Required:
Big data engineers, who have computer engineering or computer science degrees, need to know:
- Basics of algorithms and data structures, distributed computing.
- Hadoop cluster management, HDFS, MapReduce.
- Stream-processing solutions such as Storm or Spark
- Big data querying tools such as Pig, Impala, and Hive, data integration
- NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, and Hbase
- Frameworks such as Flume and ETL tools
- Messaging systems such as Kafka and RabbitMQ
- Big data toolkits such as H2O, SparkML, and Mahout.
- They must have experience with Hortonworks, Cloudera, and MapR.
How to become Big Data Engineer?
Broadly speaking, there are three distinct skill sets that must be reconciled in the data Engineer role.
- Algorithms: You understand the theory of data science, the statistics, modeling rules, and mathematics that are at the heart of any data problem. You understand how experiments are designed and measured. You understand the algorithms and theory behind data science.
- Engineering: You understand the engineering required to source, process, and store data. You should be aware of programming languages and distributed computing schemes that will help you deal with massive amounts of data at scale. You should understand the programming that applies your theories to massive datasets.
- Communication: You understand how to communicate your solutions and how to relate those solutions to business problems.
The career path would be Data Engineer → Senior Data Engineer → BI Architect → Data Architect
Data Analyst

Languages like R, Python, and SQL are part of the data analyst’s basic knowledge. Much like the data scientist role, a broad skill set is also required for the data analyst role, which combines technical and analytical knowledge with ingenuity.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Data analysts are responsible for various tasks, including visualization, munging, and processing massive amounts of data.
- They also must perform queries on the databases from time to time, looking into the key metrics of a business. They oversee data that is scraped, assuring the quality and managing it. They must interpret data and effectively communicate the findings.
- Designing and deploying algorithms, culling information and recognizing risk, extrapolating data using advanced computer modeling, triaging code problems, and pruning data are all in a day’s work for a data analyst.
- They also do presentations and work with stakeholders or non-technical stakeholders. It will be your responsibility to promote data literacy and emphasize the importance of your findings. The quality of the analysis is always paramount, but you will be evaluated mostly on the impact you are driving. This means that you always must ask, “So what?” to every insight your analysis reveals and, above all, make sure to communicate clearly what your analysis means to the end-user and what are your recommended actions.
- They also do AB testing and significance testing, where they analyze the model’s output and decide if there has been enough impact to continue the current model process, enhance it with new features or metrics and set up experiments. The goal of this role is to save the company money and time and make the business more competitive.
Unlike data scientists, data analysts are more generalists. Udacity calls them junior data scientists. They play a gamut of roles, from acquiring massive amounts of data to processing and summarizing it. This role can have a lot of freedom in the ways that you drive impact. Any trend or insight you identify and convince decision-makers to act upon is a win.
The potential downside of this freedom is that you will often not have a single clearly defined question to pursue, which can cause a lack of focus or frustration because you are not sure what to work on. Developing a sense of priorities and the ability to identify high-impact projects will be key skills.
The word “Analyst” tends to have a more junior connotation, and hence many companies (especially in the technology sector) instead use “Data Scientist”. My advice would be to not pay much attention to the word used and instead focus on the job description, team, company, and, of course, the potential salary
Skills Required:
- Data analysts are expected to know R, SAS, Python, HTML, SQL, C++, and Javascript. certification in these can easily give a boost to your job applications. You should also have good problem-solving qualities.
- They need to be more than a little familiar with data retrieval and storing systems, data visualization, and data warehousing using ETL tools, Hadoop-based analytics, and business intelligence concepts.
- Product sense, cross-discipline collaboration, AB testing, metric definition, data visualization, and stakeholder communication.
- These persistent and passionate data miners usually have strong math, statistics, machine learning, and programming background.
How to Become a Data Analyst?
SQL, R, SAS, and Python are some sought-after data analysis technologies. So, certification in these can easily give a boost to your job applications. You should also have good problem-solving qualities.
Machine learning engineers are in high demand today. However, the job profile comes with its challenges. Apart from having in-depth knowledge of some of the most powerful technologies such as SQL, REST APIs, etc., machine learning engineers are also expected to perform A/B testing, build data pipelines, and implement common machine learning algorithms such as classification, clustering, etc. This is a highly desired role and can be behind some of the most user-facing applications the internet has to offer today, such as recommendations systems or Spotify’s Discover Weekly playlist.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- To address business challenges, machine learning engineers must design and implement machine learning applications/algorithms such as clustering, anomaly detection, classification, or prediction.
- ML engineers build data pipelines, benchmark infrastructure, and do A/B testing.
- They work collaboratively with product and development teams to improve data quality via tooling, optimization, and testing. ML engineers must monitor the performance and ensure the organization’s reliability of machine learning systems.
Skills Required:
- Engineers should focus on Python, Java, Scala, C++, and Javascript.
- To become a machine learning engineer, you need to know to build highly scalable distributed systems, be sure of the machine learning concepts, play around with big datasets, and work in teams that focus on personalization.
- ML engineers are data- and metric-driven and have a strong foundation in mathematics and statistics. They are expected to have experience in Elasticsearch, SQL, Amazon Web Service, and REST APIs.
- In this role, you will sit between the data science and engineering realms: you need to have a great understanding of statistical and machine learning models and be able to implement a scalable backend solution to ship your model into production.
- This role is much more technical than the product data analyst and can be even more technical than the modeling analyst. Like the modeling analyst, this role is usually situated within a team of other technical roles such as other MLEs and data scientists. The main performance indicator will be the quality of your backend work and the ML models you ship.
- Machine learning models, statistics, back end engineering, the above three job categories likely cover most “traditional” data science jobs, but I think there is a new category of hybrid data scientist positions that are being created in response to the demand for data scientists that have data engineering and data visualization skills.
- As always, great communication skills are vital to interpreting complex ML concepts to non-experts.
How to Become a Machine Learning Engineer?
Firstly, you must have a sound knowledge of some of the technologies like Java, Python, JS, etc. Secondly, you should have a strong grasp of statistics and mathematics. Once you have mastered both, it is a lot easier to crack a job interview.
Business Intelligence (BI) Developer

BI developers design and develop strategies to assist business users in quickly finding the information they need to make better business decisions. Extremely data-savvy, they use BI tools or develop custom BI analytic applications to facilitate the end-users understanding of their systems.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Building and maintaining analysis service report models
- Using Power BI Desktop for developing dashboards, visual reports, and key performance indicator (KPI) scorecards
- Extracting various data sources and connecting, importing, and transforming data for Business Intelligence
- Implementing row-level security on data
- Should be capable of understanding the application security layer model
- Must be capable of handling project documentation and design methodology
- Should be capable of developing multidimensional models that are compatible with warehouse standards
- Must be capable of understanding business requirements and data models while taking care of the sources
- Proficient in prototyping, designing, and requirement analysis
- Should have good knowledge of secondary tools, such as SQL Data Warehouse, Azure, Visual Studio, PolyBase, etc.
- Implementing advanced-level calculations on datasets
Skills Required:
Below are some of the skills we must have if we are planning to become a BI Developer:
- Candidates should be from a computer science background and should have ample work experience in a similar field.
- They should have 4+ years of experience in data warehousing projects, data preparation, and data gateways.
- They should be experienced and familiar with other Business Intelligence analytical tools, such as SSRS, SSAS, and SSIS.
- They should have basic knowledge of JavaScript and SQL.
How to Become a Business Intelligence (BI) Developer?
A BI developer is generally required to have at least a bachelor’s degree in programming or computer science and a lot of work experience. Most have at least seven years’ professional experience. Because they have to be problem solvers, BI developers know how to mine data and how to translate this into plain English. They must also be more computer literate while also being able to remove technical jargon.
Business Intelligence Analyst

A business intelligence analyst’s fundamental job is finding patterns and value in their company and industry data.
At most companies, this is a kind of data analyst role. BI Analysts will be expected to be comfortable analyzing data, working with SQL, and doing data visualization and modeling. Like most data roles, this job also requires strong communication skills so that you can communicate your results convincingly to others at the company.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Meet with clients to identify needs and concerns
- Conduct information-gathering interviews and obtain feedback from clients and customers
- Collect data and extract data from warehouses for reporting, using querying techniques
- Analyze current data with software applications
- Create summary reports of a company’s current standings
- Present recommendations to senior management about ways to increase efficiency
- Oversee implementation of technological initiatives
- Develop new analytical models and techniques for a company to standardize data collection
Skills Required:
- Excellent communication and presentation skills in order to share recommendations with colleagues
- Superior leadership abilities, as well as the ability to work with team members on a data science project
- Creative problem-solving skills and critical thinking
- Ability to work within a diverse, global workforce that is oriented around customer satisfaction
- Database design and data architecture
- Data mining and analytics
- Data security and privacy
- Data visualization, including tools such as Tableau and Qlik
- Handle all variants of SQL
- Proficient in ETL (extract, transform, load)
- Understand which situations need Hadoop, R, and SAS and use these effectively
- Cloud computing and data storage technology, such as BigQuery and Redshift
How to Become a Business Intelligence Analyst?
Technical skills required to be a BI Analyst — The IT part of the profession places a priority on database skills. You’ll want to be proficient in database creation and maintenance and designing advanced SQL queries.
Programming skills are essential — Even the smallest companies can have immense datasets, so you’ll need programming skills to help handle the load and automate workflows. This doesn’t mean you need to spend years becoming a C++ or Java guru. You’ll mostly want to focus on Python and SQL.
Knowledge of Tableau or Power BI preferred — Excel and SQL skills are great. However, knowledge of next-generation tools will ease the transition to BI analyst. With advanced business analytics capabilities, Tableau and Power BI are renowned for their ability to identify data insights and create actionable reports.
Statistician

A statistician, as the name suggests, has a sound understanding of statistical theories and data organization. Not only do they extract and offer valuable insights from the data clusters, but they also help create new methodologies for the engineers to apply.
Statisticians collect, organize, present, analyze, and interpret data to reach valid conclusions and make correct decisions. They are key players in ensuring the success of companies involved in market research, transportation, product development, finance, forensics, sport, quality control, environment, education, and governmental agencies. A lot of statisticians continue to enjoy their place in academia and research.
The field of statistics has always been about number crunching. A strong statistical base qualifies you to extrapolate your interest in several data scientist fields. Hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), data visualization, and quantitative research are some of the core skills possessed by statisticians which can be extrapolated to gain expertise in specific data scientist fields explained in the following section of this article.
When clubbed with domain knowledge (such as marketing, risk, and actuarial science), statistics knowledge is the ideal combination to land a statistician’s work profile. They can develop statistical models from big data analysis, carry out experimental design, and apply theories of sampling, clustering, and predictive modeling to available data to determine future corporate actions.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Using statistical analysis software tools, statisticians analyze collected or extracted data, trying to identify patterns, relationships, or trends to answer data-related questions posed by administrators or managers. They interpret the results and strategic recommendations or incisive predictions using data visualization tools or reports.
- Maintaining databases and statistical programs, ensuring data quality, and devising new programs, models, or tools if required also come under the purview of statisticians. Translating boring numbers into exciting stories is no easy task!
Skills Required:
- Typically, statisticians need higher degrees in statistics, mathematics, or any quantitative subject. They need to be mini experts in the industries they choose to work in. They need to be well-versed in R programming, MATLAB, SAS, Python, Stata, Pig, Hive, SQL, and Perl.
- They need to have a strong background in statistical theories, machine learning, data mining and munging, cloud tools, distributed tools, and DBMS. Data visualization is a hugely useful skill for a statistician. Aside from industry knowledge and problem-solving, and analytical skills, excellent communication is a must-have skill to report results to non-statisticians clearly and concisely.
How to Become a Statistician?
A statistician must have a passion for logic. They are also good with a variety of database systems such as SQL, data mining, and various machine learning technologies.

Data scientists must understand the challenges of business and offer the best solutions using data analysis and data processing. For instance, they are expected to perform predictive analysis and run a fine-toothed comb through “unstructured/disorganized” data to offer actionable insights. They can also do this by identifying trends and patterns that can help the companies in making better decisions.
One of the most in-demand professionals today, data scientists rule the roost of number crunchers. Glassdoor says this is the best job role for someone focusing on work-life balance. Data scientists are no longer just scripting success stories for global giants such as Google, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
Almost every company has some sort of data-role on its careers page. Job Descriptions for data scientists and data analysts show significant overlap.
Skills Required:
- They are expected to be R, SAS, Python, SQL, MatLab, Hive, Pig, and Spark experts.
- They typically hold higher degrees in quantitative subjects such as statistics and mathematics and are proficient in Big Data technologies and analytical tools.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Being a data scientist is not only about data crunching. It’s about understanding the business challenge, creating valuable, actionable data insights, and communicating their findings to the business.” Data scientists come up with queries.
- Along with predictive analytics, they also use coding to sift through large amounts of unstructured data to derive insights and help design future strategies.
- Data scientists clean, manage and structure big data from disparate sources. These “curious data wizards” are versatile, to say the least, they enable data-driven decision-making often by creating models or prototypes from trends or patterns they discern and by underscoring implications.
How to Become a Data Scientist?
To become a data scientist, you have to be an expert in R, MatLab, SQL, Python, and other complementary technologies. It can also help if you have a higher degree in mathematics, computer engineering, etc.

Computer vision engineering is an interdisciplinary (scientific) field that deals with how computers can be made to gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of technological advancements & engineering, it seeks to automate tasks that the human visual system can do. A computer vision Engineer is concerned with the automatic extraction, analysis, and understanding of useful information from a single image or a sequence of images. It involves the development of a theoretical and algorithmic basis to achieve automatic visual understanding. Yet another field related to computer vision is signal processing. Many methods for processing one-variable signals, typically temporal signals, can be extended naturally to processing two-variable or multivariable signals in computer vision.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Developing image analysis algorithms and deep learning architectures to solve problems
- Designing and creating platforms for image processing and visualization
- Knowledge of computer vision frameworks and libraries
- Understanding of TensorFlow or PyTorch for dataflow programming
- Proficiency with vector quantization and clustering to build search engines and systems
- Understanding of computational geometry, statistics, and linear algebra
- Computer vision engineer is concerned with automatically extracting, analyzing, and understanding useful information from a single image or sequence of images.
- It involves the development of a theoretical and algorithmic basis to achieve automatic visual understanding.
- Develop computer vision solutions; gain experience with deep learning; translate demonstrable technology.
- Understanding of the working of a web-based application.
- Basic understanding of REST APIs and their concepts.
Skills Required:
The skills needed for computer vision jobs can be divided into three categories:
- Computer Vision knowledge:
The basics of computer vision are built upon digital image processing. So, you need to learn the basics of the DIP first. Then you can move forward to read computer vision topics like pattern recognition and 3D geometry. You need to know linear algebra to be able to fully understand some concepts of computer vision like dimensionality reduction. After understanding the fundamentals of computer vision, you should also build your knowledge in deep learning, especially in Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), which is state of the art in CV today. - Programming:
Python will be enough for design and prototyping, but if you want to do some embedded work, you should also be familiar with C++. - CV tools:
OpenCV is the main tool for computer vision. You have to know it. You will never be able to know all its functions, but you should know what tools are available in it and how you can use them. Another tool that you need to be familiar with is a deep learning framework. You can start with Keras, which is the easiest to learn, and then learn either Tensorflow or PyTorch.
How to Become a Computer Vision Engineer?
- Complete a relevant degree program. Start with a Bachelor of Science in Information Systems, Computer Science, or a similar discipline. This will give you a good understanding of the importance of testing, system architecture, and technology development.
- Earn a postgraduate qualification. Computer vision engineers need specialist knowledge of their field. A master’s in computer engineering or computer science allows you to focus on specific courses that will add to your understanding of development environments, object-oriented software, and other relevant skills.
- Gain experience with real-world projects. Most computer vision engineers will work in software development or computer engineering to give them the transferable skills required to specialize in computer vision engineering.
Natural Langauge Processing(NLP) Engineer
Natural language processing (NLP) comes from an amalgamation of computer science, Information sciences, AI, and linguistics. NLP focuses on the interaction between computers and human languages. While computers handle structured datasets, they require a little help when it comes to human languages with hundreds of different languages and dialects, all with their own set of grammar rules, slang, terms, and syntax. Ever wonder how Google or Alexa can understand what you’re saying? That’s NLP in play! And therefore, NLP Engineers are responsible for the programming behind technology’s ability to process and analyze natural language data.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Design and develop natural language processing systems
- Define appropriate datasets for language learning
- Use effective text representations to transform natural language into useful features.
- Develop NLP systems according to requirements
- Train the developed model and run evaluation experiments
- Find and implement the right algorithms and tools for NLP tasks
- Perform statistical analysis of results and refine models
- Constantly keep up to date within the field of Machine Learning & Deep Learning
- Maintain NLP libraries and frameworks
- Implement changes as needed and analyze bugs
Skills Required:
- Understanding of text representation techniques, algorithms, statistics
- Machine Translation & Compilers experience
- Knowledge of Machine Learning and Deep Learning frameworks and libraries
- Familiar with Big Data frameworks — Spark, Hadoop
- Text classification & clustering skills
- Programming skills — Python, Java, and/or R
- Strong problem-solving abilities
- Syntactic & Semantic Parsing
- Knowledge of CI/CD pipelines
- Strong communication skills
How to Become an NLP engineer?
A large number of NLP Engineers come from an academic background. In order to become an NLP Engineer, getting a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science, Mathematics, Science, Physics, or similar is recommended.
- The exact entry requirements are different depending on the nature of the role within a company. But industry experience and managing statistical analysis on large datasets would be necessary as well as some software engineering experience.
- Certifications are also a good way to gain a strong foothold in the field. Here are a few great online options to consider when learning natural language processing:
- Standford Online Learning — NLP
- Udacity NLP Nanodegree

MLOps is communication between data scientists and the operations or production team. It’s deeply collaborative in nature, designed to eliminate waste, automate as much as possible, and produce richer, more consistent insights with machine learning. ML can be a game-changer for a business, but without some form of systemization, it can devolve into a science experiment. MLOps brings business interest back to the forefront of your ML operations. Data scientists work through the lens of organizational interest with clear direction and measurable benchmarks. It’s the best of both worlds.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- The role of the ML Engineer is to use their knowledge of ML/AI and combine it with programming and software engineering skills to enable easier use of and access to said models and analyses.
- Translating the work of data scientists from environments such as python/R notebooks analytics applications.
- Creation of web services/APIs to serve ML/AI model results and enable access to customers or internal teams.
- Automating model training and evaluation processes.
- Automating feature engineering, ensuring data for model training is cleaned and readily available and facilitating the flow of data between ML/AI models and an organization’s data systems.
Skills Required:
- Research and implement MLOps tools, frameworks, and platforms for our Data Science projects.
- Work on a backlog of activities to raise MLOps maturity in the organization.
- Proactively introduce a modern, agile and automated approach to Data Science.
- Conduct internal training and presentations about MLOps tools’ benefits and usage.
- Wide experience with Kubernetes is a must-have.
- Experience in the operationalization of Data Science projects (MLOps) using at least one of the popular frameworks or platforms (e.g., Kubeflow, AWS Sagemaker, Google AI Platform, Azure Machine Learning, DataRobot, DKube).
- Good understanding of ML and AI concepts. Hands-on experience in ML model development.
- Proficiency in Python used both for ML and automation tasks. Good knowledge of Bash and Unix command-line toolkit.
- Experience in CI/CD/CT pipeline implementation.
- Experience with cloud platforms — preferably AWS — would be an advantage.
- Excellent communication skills in English, both verbal and in writing.
How to Become an MLOps Engineer?
We need to study the general concepts of the Machine Learning algorithm(s) used to understand the business problem and the Data Science solution. Also, there is an overlap between Data Scientists and MLOps Engineers. They often work closely together to achieve the company’s ultimate goal of running a beneficial Machine Learning algorithm or Data Science model.
What role is right for you?
The above roles can be distinguished by an impact vs. methods vs. platforms trichotomy. If you are a talented data scientist interested in driving insights and impact on a particular product or part of the business, with less focus on the methodology and techniques used, then you might be more suited for the product data analyst or business intelligence positions.
- If you are interested in always being near the nexus of the latest machine learning models and methods and are excited to apply them to your company’s vast data sources, then you might be better suited to the modeling analyst and machine learning engineer positions.
- Finally, if you’re motivated by taking a more horizontal role in your organization, to educate and enable other teams to do their work better, then you might be interested in the data-services-as-a-platform roles, such as the platforms & tools developer.
- If a job listing caught your eye and you aim to understand better what type of data science role it is, read the job description and try to see if they emphasize impact, methods, or platforms. Also, ask the hiring manager who your stakeholders will be and how your performance will be evaluated.
If you’re entering the data science job market for the first time, Welcome! I hope this guide can help give you more clarity on the types of positions and help you identify the opportunities that are best suited to your talents and interests. Let me know in the comments if you’re finding roles that don’t fit into the impact vs. methods vs. platforms trichotomy.
If you’re someone with experience in the data science job market, how have you seen data science roles take shape in your companies?” Thanks for reading!
If you like what we do and want to know more about our community 👥 then please consider sharing, following, and joining it. It is completely FREE.
Also, don’t forget to show your love ❤️ by clapping 👏 for this article and let us know your views 💬 in the comment.
Join here: https://blogs.colearninglounge.com/join-us

